GUT HEALTH: THE KEYS TO BOOST YOUR BODY'S IMMUNE SYSTEM

FIND OUT HOW your gut affects your health and well-being … and what you can do about it.
A MANUAL'S SOLUTIONS FOR FOOD INTOLERANCES, LEAKY GUT, CANDIDA AND CROHN'S DISEASE
In this comprehensive article (just contents, you will get helpful articles covering each part), we will : discuss why your gut health is important for your overall health, how your gut connects to your well-being, provide actionable tips you start using today for better gut health and introduce the gut-healing diet of Leaky Gut Syndrome. Whether you are a student, practitioner, or just a damn good person looking to optimize your health, you’ll learn everything you need to know to become the master conductor of your GI health in this post.
Learn more: Gut Health, Why It Matters
Gut health is the cornerstone of overall health, and affects more than digestion. It affects your immune system, mood, energy and even skin condition. Let’s explore why your gut health is so important and how it influences many areas of your life.
1. The Function of the Gut during Digestion
The gut processes food and absorbs nutrients. It’s an elaborate construction that involves the stomach, small intestine and large intestine. Any disruption in this balance can result in digestive problems (like gas, constipation, or diarrhea). And after birth… A healthy gut means that your body can absorb all the nutrients it needs, to keep you energized and bright.
-
3 Digestive Issues: Factors such as consuming an unhealthy diet, stress, and the way you live may all affect your beneficial bacteria’s balance to lead to diseases like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), acid reflux, or Crohn’s disease.
-
Nutrient Absorption: A healthy gut allows you to absorb important vitamins and minerals, like B vitamins, iron and magnesium, important for overall good health.
2. Gut Health and the Immune System The microbes are definitely on the move!
Do you know more than about 70% of your immune system is in your gut? The lining of the gut is populated with immune cells that help the body identify dangerous pathogens and defend against infections. A healthy gut microbiome is a good mediator of this immune response to keep your body from overreacting to benign substances (like pollen) and to keep autoimmunity in check.
-
Prevention of illness : A healthy gut microbiome can help protect against viruses and bacteria, helping to ward off the illnesses.
-
Preventing Illness: A healthy gut microbiome can help protect against viruses and bacteria, helping to ward off the illnesses. Inflammation: Long-term inflammation in the gut can cause conditions such as autoimmune diseases, in which the immune system starts attacking the body’s own tissues.
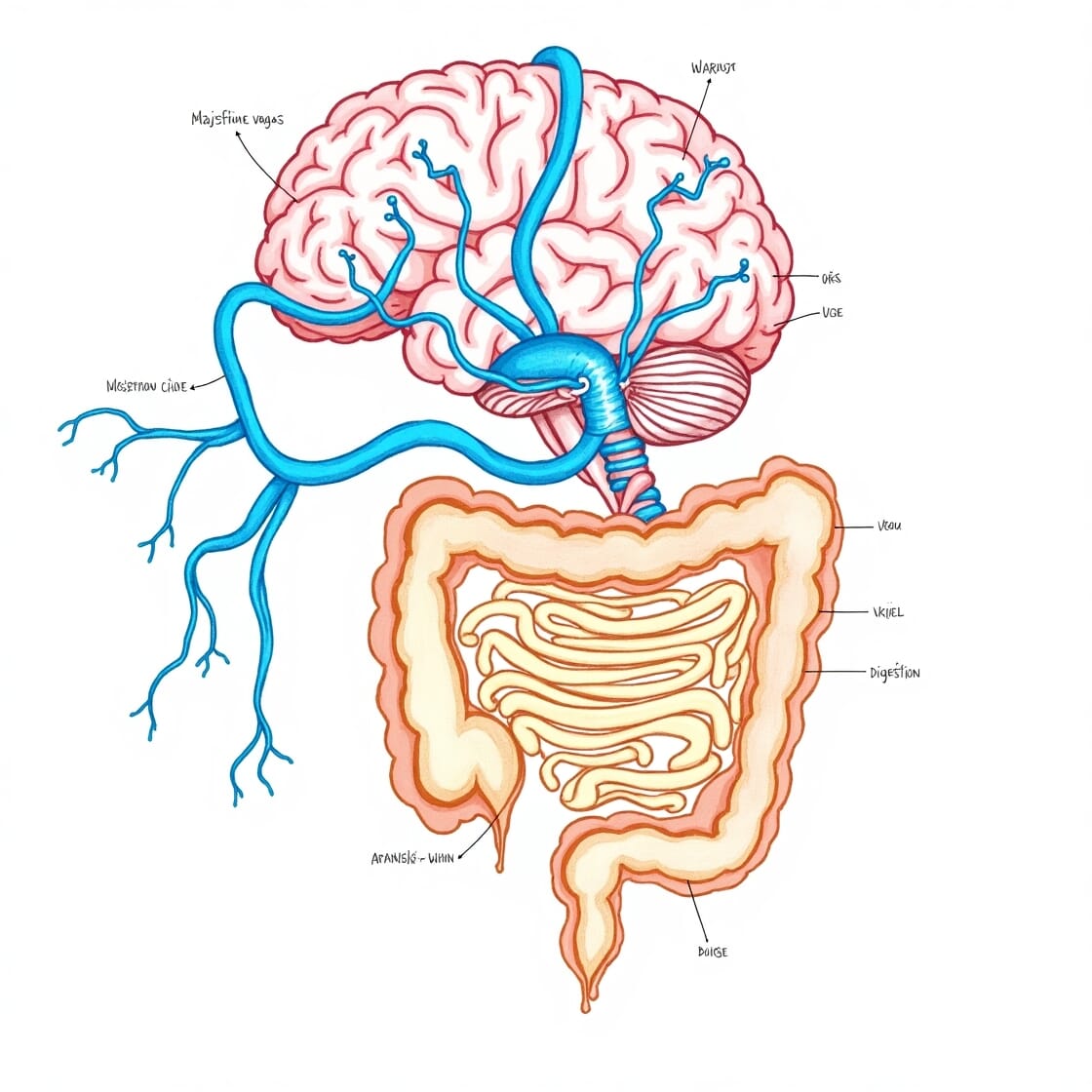
3. Gut-Brain Connection: Mental Health
You gut is frequently called the the “second brain” because it manufactures neurotransmitters such as serotonin — which is responsible for mood and emotional well-being. Poor gut health can affect your mental state and lead to symptoms of stress, anxiety and even depression.
- Regulating Mood: The gut in which about 90% of serotonin is produced. When there’s an imbalance of gut bacteria, so too can the levels of serotonin, the neurotransmitter that’s crucial to your mood.
- The Vagus Nerve: This nerve runs from the brain to the gut, so signals can travel to and from, hence the gut and the brain are also very connected.
 4. The Relationship Between The Gut And Skin Conditions
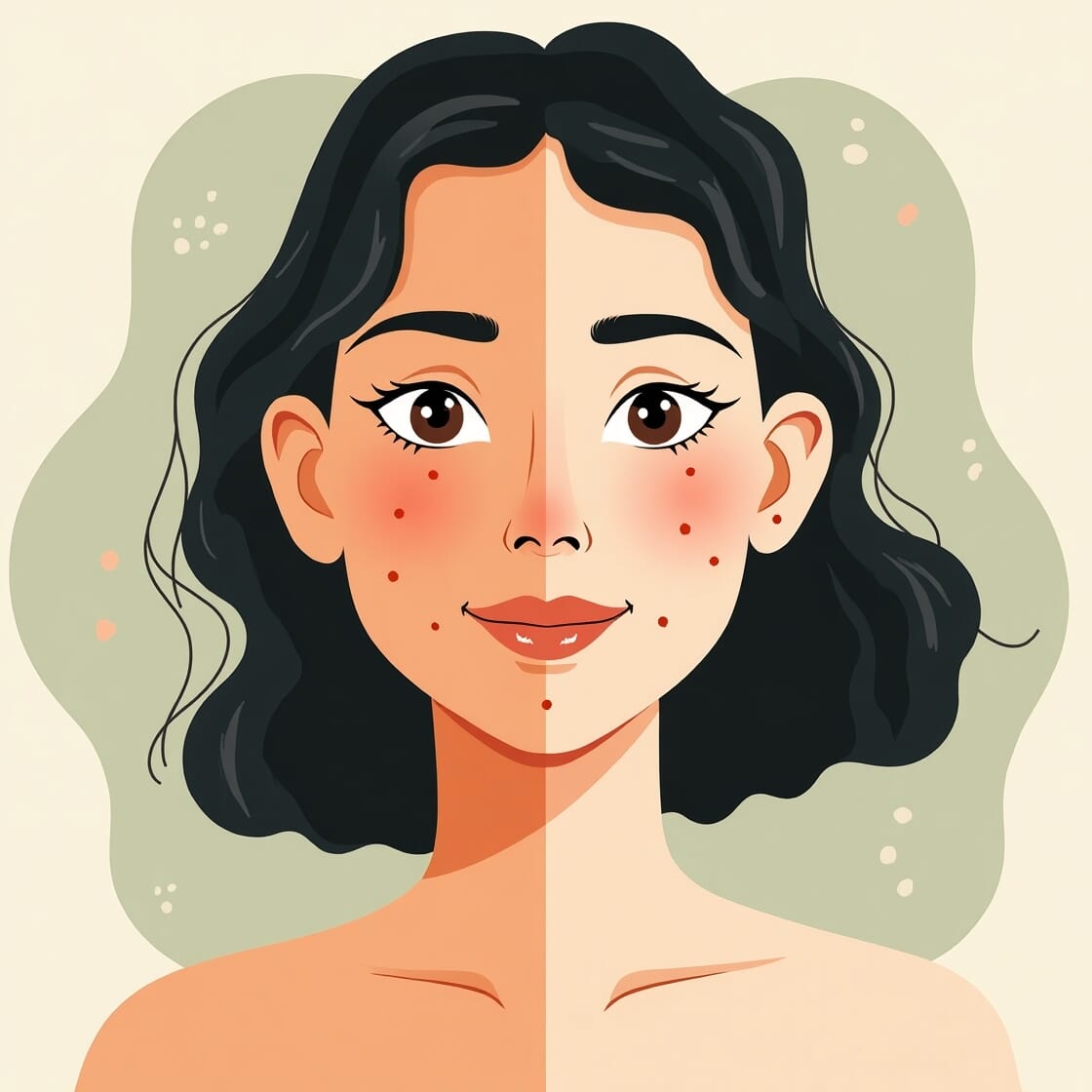
4. The Relationship Between The Gut And Skin Conditions
A healthy gut also reflects on your skin. When the microbiome of your gut is out of balance, it can cause inflammation, manifesting as acne, eczema and psoriasis. Your skin is frequently a mirror to what’s happening internally.
- Skin Inflammation: A poor gut can increased the levels of toxins circulating in your blood causing inflammation in your skin and can manifest as acne or other skin problems.
- Clear Skin – Balancing the bacteria in your gut through diet and probiotics can help to reduce inflammation and restore proper digestion, which in turn can lead to clearer skin.

5. The Impact of Diet on Gut Health
What you eat directly affects the health of your gut. A diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods promotes a healthy microbiome, while a diet high in sugar, processed foods, and unhealthy fats can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to digestive and systemic health problems.
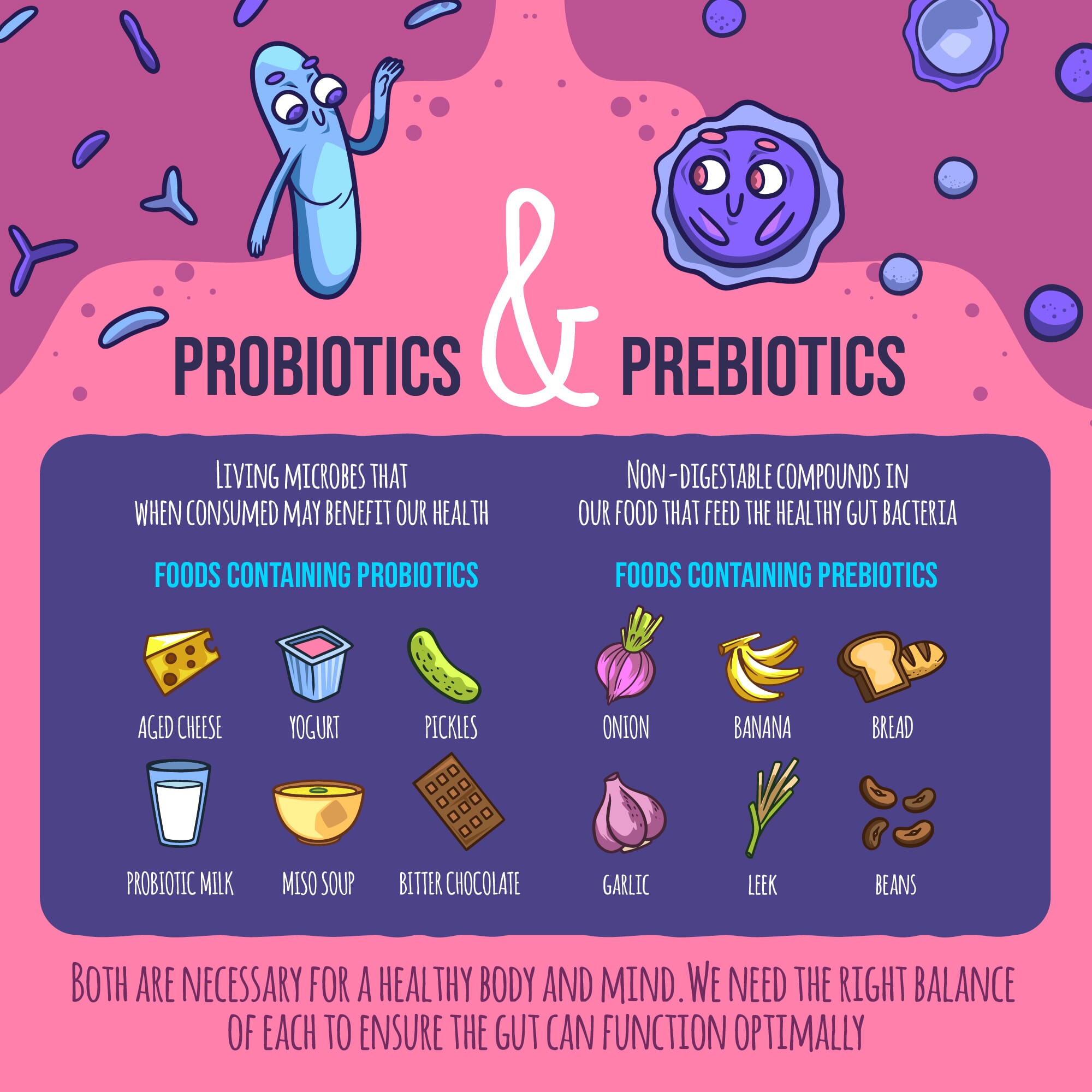
- Fiber and Prebiotics: Foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables act as fuel for beneficial gut bacteria.
- Probiotics: Fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain probiotics that help replenish healthy bacteria in the gut.
%20versus%20foods%20that%20disrupt%20gut%20health%20(e.g.%2C%20sugary%20snacks%2C%20processed%20foods).jpg)
6. Gut Health and Weight Management
Emerging research suggests that gut health plays a significant role in regulating metabolism and controlling weight. An imbalance in the gut microbiome may contribute to obesity, while a balanced microbiome can help maintain a healthy weight.
- Gut Bacteria and Appetite: Certain gut bacteria influence how your body processes food and signals hunger, which can impact eating behaviors and weight management.
- Fat Storage: An imbalanced gut microbiome may cause your body to store more fat, while a healthy gut helps regulate energy use and fat burning.